C Programming Recursion
C Recursion
A function that calls itself is known as a recursive function. And, this technique is known as recursion.
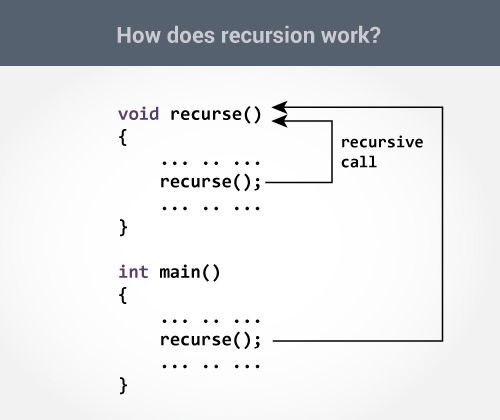
How recursion works?
void recurse()
{
... .. ...
recurse();
... .. ...
}
int main()
{
... .. ...
recurse();
... .. ...
}
The recursion continues until some condition or usually called a base case is met or to prevent it.
To prevent infinite recursion, if...else statement (or other constraints) can be used to stop the recursive call.
Example: Sum of Natural Numbers Using Recursion
#include <stdio.h>
int sum(int n);
int main()
{
int number, result;
printf("Enter a positive integer: ");
scanf("%d", &number);
result = sum(number);
printf("sum = %d", result);
return 0;
}
int sum(int num)
{
if (num!=0)
return num + sum(num-1); // sum() function calls itself
else
return num;
}
Output
Enter a positive integer:3 sum = 6
Initially, the
sum() is called from the main() function with number passed as an argument.
Suppose, the value of num is 3 initially. During next function call, 2 is passed to the
sum()function. This process continues until num is equal to 0.
When num is equal to 0, the if condition fails and the else part is executed returning the sum of integers to the
main() function.
Comments
Post a Comment